
When the kidney cells become malignant( cancerous) which forms a tumor and grow out of control is called kidney cancer.
Causes
There is no specific cause but some risk factors include smoking, obesity, hypertension, heredity, exposure to cadmium or specific homicides etc.
Symptoms
In the early stages, kidney cancer does not show any symptoms, in later stages blood in urine or cola-colored urine, pain in the back, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, tiredness are seen.
Diagnosis
Urine and blood test to detect kidney function , Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT and MRI scan with IVP (Intravenous Pyelogram)- injecting a dye that travels to the urinary tract and highlights any tumor, in rare cases renal arteriogram is performed.
Non Surgical Treatment
For some alternative options can be used to destroy small tumour’s without surgery such as-
Cryoablation:
Killing cancer cell by cooling them down, usually done by inserting a hollow needle into the kidney through the skin and injecting cold gas.
Radio Frequency Ablation:
Killing the tumor cells by using electricity by using a special probe inserted through the skin in to the kidney. An electric current is run through and causing the cells to heat up or burn.
Surgery is the first step in most cases, the aim is to remove the entire tumor from the kidney.
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy
It is most common surgery which is done through a small incision in the abdominal wall and using a laparoscope or robotically assisted laparoscope to remove the entire kidney, adrenal gland and surrounding tissue including nearby lymph tissue.
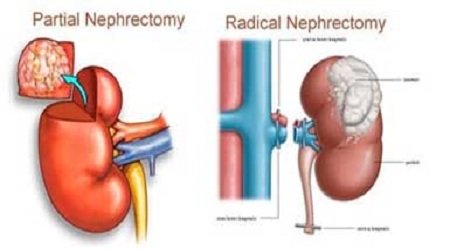
Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy
In cases of small tumors the surgeon remove the tumor and small margin of healthy tissue surrounding it instead of entire kidney, it is performed laparoscopically or robotically assisted by making a small incision on the abdominal wall.
Your Search for Urocare Ends Here.
Makstar Super Specialty Health CenterNo 1, Ex Servicemen Colony,RT Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560032
Mobile: +91- 63644 27341
urocarebangalore@gmail.com
Powered By Gladias Consulting Pvt Ltd